This weekend, Bitcoin's mempool cleared for the first time in two years. This allowed transactions with the lowest possible fee rate, 1 sat/vByte, to be included in blocks. Additionally, multiple half-empty blocks were mined, as there weren’t enough pending transactions to fill the available space.

This event reignited the debate about Bitcoin’s “security budget”, with some critics arguing that if there aren’t enough on-chain transactions, miners will go bankrupt, and the network will lose security. However, this analysis is incorrect for several key reasons:
Miners Earn Money Even Without Transaction Fees
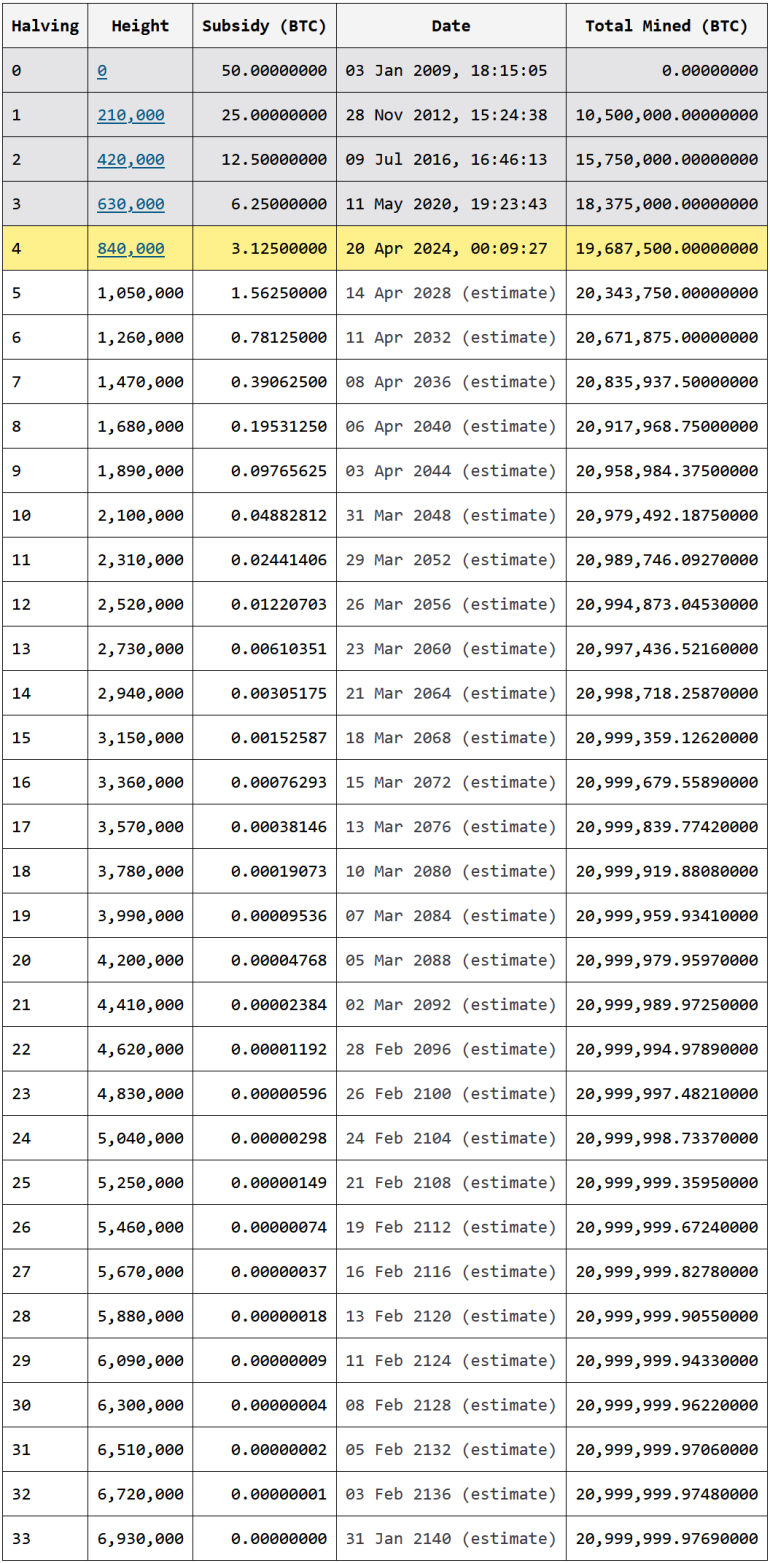
Every time a miner finds a block, they receive a subsidy in newly created Bitcoin, regardless of how many transactions are included. Currently, this subsidy is 3.125 BTC per block (~$300,000 USD).
Even if, in the future, the network relied solely on transaction fees, this won’t be an issue for several decades.
Mining is a Self-Balancing System
Bitcoin has a difficulty adjustment mechanism that constantly balances miner profitability. Every 2,016 blocks, the mining difficulty is adjusted to ensure blocks continue being mined approximately every 10 minutes.
If mining becomes unprofitable, some miners turn off their machines, leading to a decrease in difficulty, allowing the most efficient miners to continue operating. This equilibrium has kept mining healthy over time.
Miners Are Earning More Money Than Ever
Despite concerns, miners are earning approximately $48 million per day, the highest level since the April 2024 halving. Over time, miner revenues have shown an upward trend, even with the block subsidy being halved every four years.
Conclusion
The recent mempool clearance is not a sign of crisis but rather an example of Bitcoin’s natural equilibrium. The network’s security does not rely solely on transaction fees but on a well-designed economic model, which has proven to be resilient and sustainable over time.








